Optimizing Commercial Rabbit House Design for Maximum Productivity
For rabbit farms in different regions, the climate conditions vary greatly, the economic foundations vary, and the commercial rabbit house design forms are also different. The design form and structure of commercial rabbit houses mainly depend on factors such as breeding purpose, breeding method, breeding scale and economic affordability. Small-scale commercial rabbit production and commercial rabbit breeding of sideline nature should adopt simple commercial rabbitry design. Old sheds or idle houses can be used for free-range or penned breeding. For commercial rabbit breeding of a certain scale, it is advisable to design a more standardized semi-open rabbit house or closed rabbit house for cage breeding to facilitate daily management.
Placing rabbits in commercial rabbit cages for farming, known as commercial rabbit cage farming, is an ideal breeding method. Compared to other methods such as free-range, pen, and cave farming, cage farming offers better control over the rabbits' living environment. It simplifies feeding management, breeding, and disease prevention, promoting the rabbits' growth and improving fur quality. Therefore, it is a farming method worth promoting.
Main Types of Commercial Rabbit House Design
Shed rabbit house
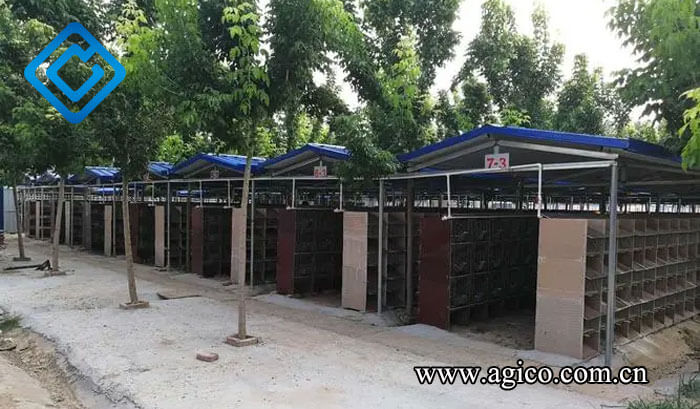

Shed rabbit house adopts a design with a roof but no walls around it. There are only rabbit cages or mesh fences under the roof. Its characteristics are protection from the sun and rain, high air flow rate, good ventilation, and low cost. Because the temperature inside the shed changes with the outside temperature, it is currently widely used in hot areas.
Semi-open rabbit house
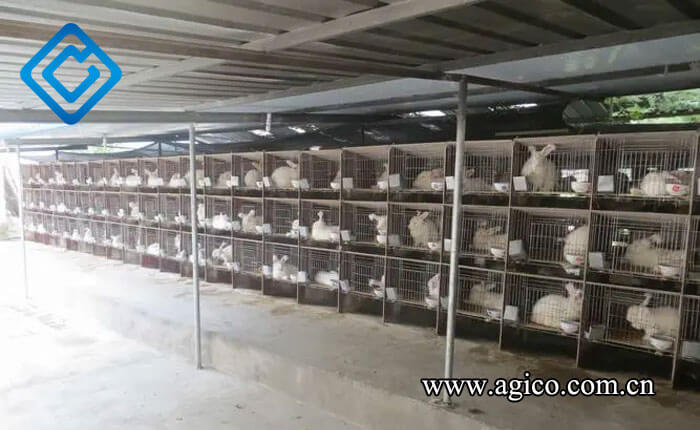

The semi-open rabbit house adopts a one- or two-side wall-free design, and the back wall of the rabbit cage also serves as the wall of the rabbit house. There are two types of rabbit houses: single-row and double-row. This rabbit house has a simple structure, low cost, plenty of sunlight, good ventilation, and convenient management. However, it is difficult to keep warm in winter and can be susceptible to predator attacks. The semi-open commercial rabbit cage design is suitable for small and medium-sized rabbit farms and professional households.
Closed rabbit house
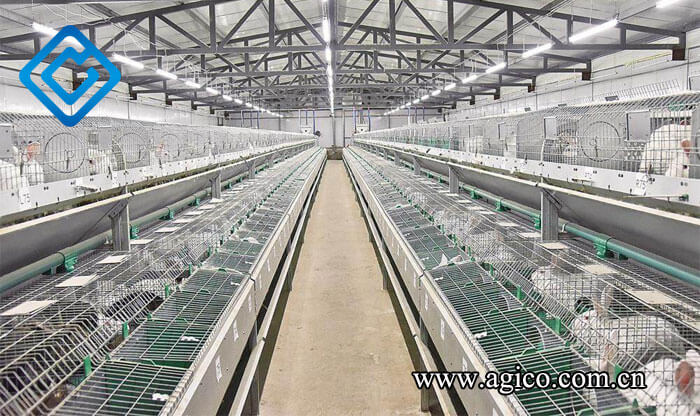

The closed rabbit house is designed with walls and no windows on all sides. The microclimate in the rabbit house is completely automatically adjusted by special devices and can realize automatic feeding, automatic drinking water and automatic feces cleaning. This commercial rabbitry design can achieve a high and stable weight gain rate, control the consumption rate of feed, and help prevent the spread of various diseases. However, it needs to be equipped with a series of climate control devices, which is expensive. At present, closed rabbit houses are mainly used for meat rabbit farming and experimental rabbit breeding.
Indoor Cage-style rabbit house
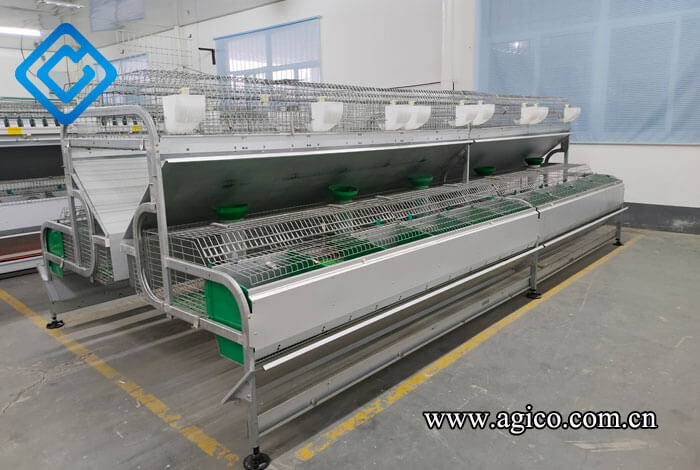

European rabbit cages
The indoor cage-style rabbit house features walls on all sides and an A-frame roof. Windows and ventilation holes are placed on the north and south walls, while doors and passageways are located on the east and west walls. The advantages of this commercial rabbit house design include good ventilation, easy management, and efficient heat retention and insulation.

Stacked rabbit cages
Inside the rabbit house, multiple rows of European-style rabbit cages or stacked rabbit cages can be placed according to the breeding needs. However, due to the high breeding density and potentially poor natural ventilation, it requires specialized ventilation and lighting equipment. This type of rabbit house is suitable for large-scale rabbit farms.
Hill Cave-style rabbit house
For this type of rabbit house, choose a sunny, dry, and hard-soiled hill. Modify the south-facing cliff face to be perpendicular to the ground. After the surface dries, build a 40 cm high platform against the cliff base. On top of the platform, construct three layers of rabbit cages with bricks and stones. The orientation of the rabbit house should consider sunlight and the prevailing local wind direction, with the long axis of the hutch facing the summer prevailing wind. This rabbit house is suitable for commercial rabbit farming in hilly areas.
Key Environmental Factors in Commercial Rabbit House Design
The environmental factors in commercial rabbitry design refer to the external conditions that impact the rabbits' living and production. Many factors influence the house environment, such as temperature, humidity, ventilation, light, noise, dust, and greenery.
Temperature
Rabbits have poorly developed sweat glands and dense fur, and young rabbits have weak self-regulation of body temperature. Therefore, the ambient temperature significantly affects their normal living and commercial rabbit production. The suitable temperature for baby rabbits is 30-35°C, for young rabbits is 20-25°C, and for adult rabbits is 15-20°C. If the hutch temperature exceeds 30°C or falls below 5°C, it can adversely affect the growth and development of young rabbits, the breeding of breeding rabbits, and the birth of kits. Therefore, the design of commercial rabbit houses must consider local climate conditions and incorporate effective temperature control mechanisms.
Humidity
Excessive humidity will increase the harm of high and low temperatures to rabbits. Too little humidity is not conducive to the growth of fur and skin and the improvement of fur and skin quality. The most suitable relative humidity for rabbit houses is 60%-65%, and generally should not be lower than 55% or higher than 70%. Therefore, the construction of rabbit houses must take into account the drainage performance of the ground, especially the manure and urine ditch, and the hygroscopicity of cage-building materials.
Ventilation
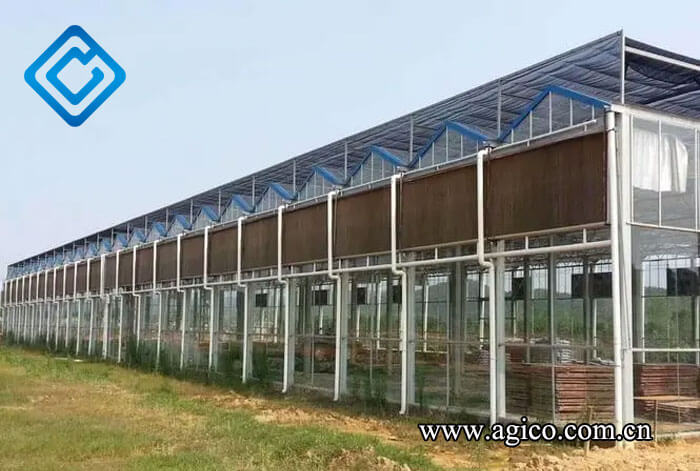

The ventilation methods of rabbit houses can generally be divided into natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation. Small farms often use natural ventilation, which uses air convection of doors and windows or exhaust holes on the roof for adjustment. Large and medium-sized rabbit farms often use exhaust fans and other equipment for mechanical ventilation. There is a standard for suitable wind speed in rabbit houses, which is 0.4 m/s in summer and 0.1-0.2 m/s in winter.
Lighting
Production practice shows that rabbits have different requirements for lighting. Generally speaking, breeding rabbits require longer lighting, preferably 14-16 hours of lighting per day, which is manifested by high conception rate, large litter size, and the best breeding effect. For fattening Rex rabbits and meat rabbits, the lighting time should not be too long, and the best effect is 10-12 hours of lighting per day. Small rabbit farms generally use natural lighting, large and medium-sized rabbit farms, especially intensive rabbit farms, should use artificial lighting or artificial supplementary lighting. Incandescent light is better, 3-4 watts per square meter of ground, and the height of the lamp is generally 2-2.5 meters from the ground.
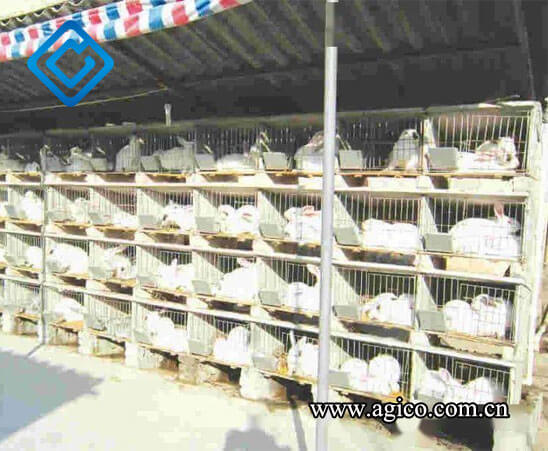

Natural lighting in rabbit house
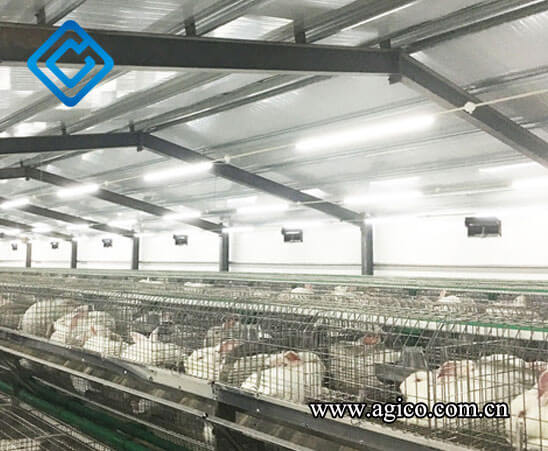

Rabbit house equipment lighting
Commercial rabbit house design plays a vital role in the rabbit breeding industry. Through reasonable space configuration and scientific environmental control, not only can the health level and production efficiency of rabbits be improved, but also higher economic benefits can be brought to the farm. Whether it is small-scale sideline breeding or large-scale commercial breeding, the appropriate rabbit house design form should be selected according to the specific situation, and continuous improvement and optimization should be made to adapt to changes in market demand and technological development.